[Syntax] 3. Clause and Movement
4.1 The I-node
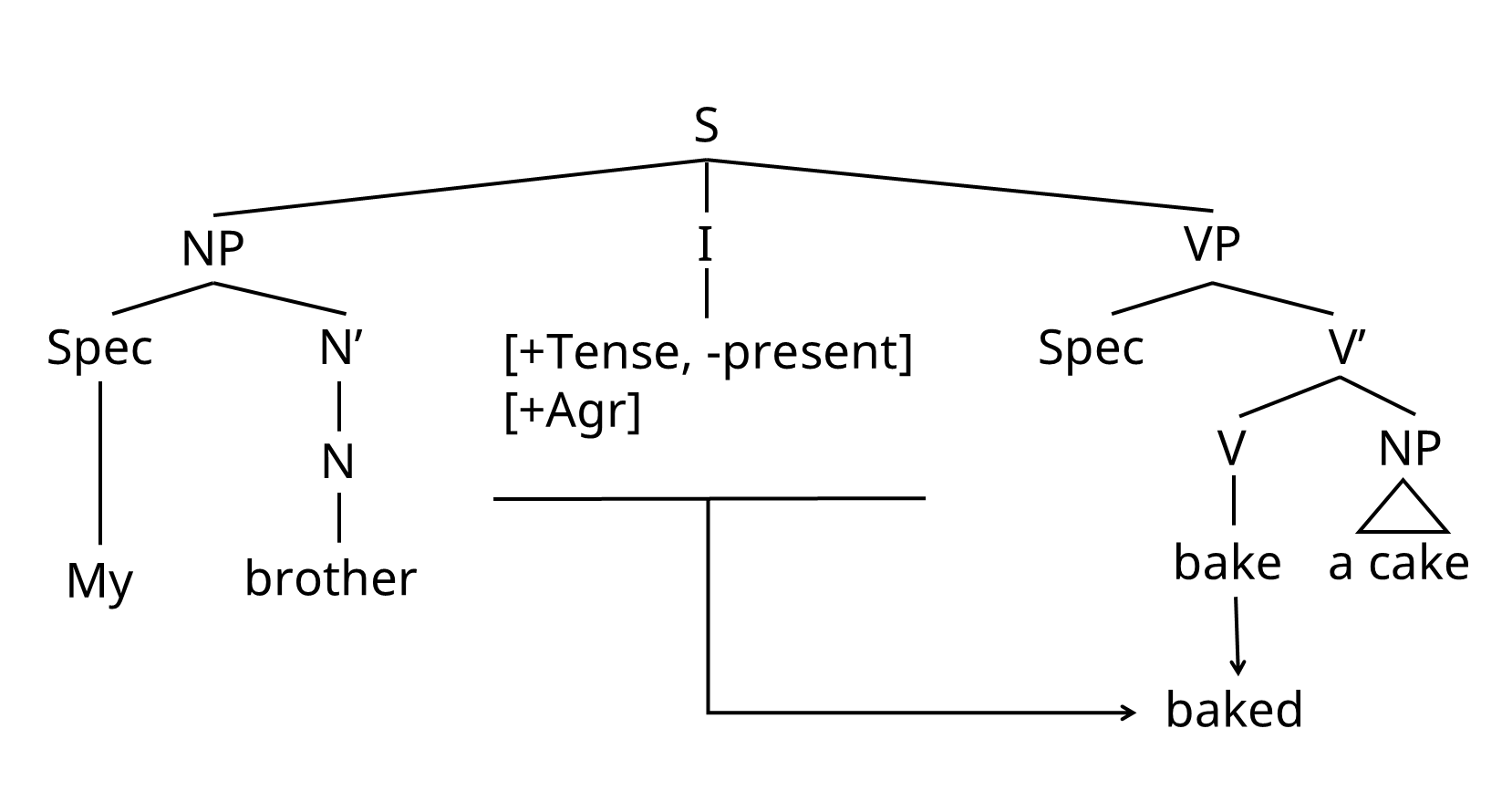
(1) My brother baked a cake.
동사 bake 는 어떻게 과거형 시제를 얻을까? S에 의해 immediately dominated 되어지는 I node가 있고, 이 곳에서 동사는 시제, 주어와 동사의 수 일치 어형을 얻는다.

- Finite clauses: [+Tense, ±present] [+Agr]
- Nonfinite clauses: [-Tense] [-Agr]
(4)
(5) She wanted [her brother to bake a cake].
(6)

Inflectional element 외에도 Auxiliary verbs 도 I-node에 들어간다.
Auxiliary verb가 VP가 아닌 I에 해당된다는 증거
(7) My brother will bake a cake.
(8) My brother will not bake a cake.
▷ negative element는 VP의 Spec자리에 오는데, VP 안에서는 Spec인 not보다 더 앞에 will이 위치할 수 있는 자리가 없다.
(10) a. Perhaps my brother will not make a cake.
b. My brother perhaps will not bake a cake.
c. My brother will perhaps not bake a cake.
d. My brother will not bake a cake perhaps.
▷ Sentence adverbs 는 S에 의해 immediately dominate 되는 자리에 위치하는데, 이 S-adverbs가 modal verb와 VP의 Specifier 사이에 위치할 수 있는 걸로 보아, modal verb는 I-node에 위치한다고 볼 수 있다.
4.2 Affix Movement vs. V Movement
(1) John annoys me
어떻게 I에 있던 Tense/Agreement inflections 이 VP의 Head인 V에 위치하게 될까? 이 질문에 대한 두 가지의 답이 있다.

(2) 첫 번째는 Affix가 VP로 이동했다는 이론
(3) 두 번째는 Verb가 I 로 이동했다는 이론 (I가 비어있는 경우)
4.2.1 V Movement Analysis
1. Negation

(6)의 경우, negative element가 Moday may 다음에 위치하지만 VP에 있는 Aspectual Auxiliaries have 와 be 앞에 위치한다.
하지만 (7)을 보면, have 와 is 는 원래 VP에서 생기지만, I가 비어있는 경우 V movement에 의해 I로 옮겨간다.
2. Adverb distribution
S-adverbs(certainly, probably, definitely 등)은 S의 immediate constituent로만 위치할 수 있다.
(11)(a) George will probably have been working
(b) *George will have probably been working
(c) *George will have been probably working
S-adverb probably 가 will 과 have 에는 위치 가능, 따라서 I와 VP의 경계에 위치한다고 볼 수 있다.
(13)(a) George has probably been working
(b) *George has been probably working
그렇다면 (13)의 경우, 왜 has와 been 사이에 부사가 위치 가능할까? 이를 V movement가 설명해줄 수 있다.
(22) He will not have broken the mirror.
Movement of aspectual auxiliary는 V 에서 I로 이동, 단 I자리를 차지하고 있는 modal verb가 없는 경우에만 이동
4.3 I Movement I-to-C Movement
흔히 알려진 Subject-Auxiliary Inversion

4.3.1 Movement Analysis
1. Gap argument
(3)(a) *Will [S he [I can] tell the truth]?
(b) *Will [S he [I to] tell the truth]?
No refilling condition: Modal will 은 I 에서 C로 movement를 거쳤기 때문에, 원래의 I 는 can/to 와 같은 다른 요소들로 채워질 수 없다.
2. Subcategorization
(4) John can go/*going/*gone/*goes/*went to the party
can과 같은 Modal Auxiliary는 infinitival VP Complement Complement를 subcategorize 한다.
(5) Can [S John go/*going/*gone/*goes/*went to the party]?
Modal이 inverted 된 경우 (I movement가 일어난 경우)에도 마찬가지로 VP는 Modal Auxiliary 의 영향을 받는다.
3. Have Contraction
Vocalic contraction of have down to /v/ (have의 축약형)은 두 가지 조건이 있다.① vowel이나 diphthong 으로 끝나는 대명사 뒤에서만 축약이 발생,② 대명사와 have 사이에 gap이 있는 경우 발생하지 X
(7)(a) Should I have/*I've called the Police?
(b) Will we have/*we've finished by 4 o'clock?
(c) Would you have/*you've wanted to come with me?
(d) Could they have/*they've done something to help?
I Movement에 따르면, 조동사 should, will, would, could 는 I로부터 이동했기 때문에 대명사와 have 사이에는 gap이 존재하고, 이는 have contraction을 설명할 수 있다.
⇒ Have contraction is blocked by the presence of a 'gap' between the Pronoun and have.⇒ Modals in I are moved into an empty C. (= the landing-site for inverted Modals is an empty C.)
4.4 Wh-Movement
(1) What will you buy?
위와 같은 일반 의문문에는 세 가지 주목할만한 법칙이 존재한다.
① 문장 맨 앞에 존재하는 wh-element
② Subject-Auxiliary Inversion
③ 동사 buy의 목적어가 없음
⇒ The wh-element is moved from the DO position following the main verb to the beginning of the sentence.
(4) What will he do?
(5)

(6)

'English Education > Syntax' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Syntax] 4. Constituency (2) (0) | 2020.09.16 |
|---|---|
| [Syntax] 4. Constituency (1) (0) | 2020.09.14 |
| [Syntax] 3. Clause and Movement(2) (0) | 2020.09.14 |
| [Syntax] 2. X-Bar Syntax: Cross-Categorial Generalisations (0) | 2020.09.09 |
| [Syntax] 1. Thematic roles (Theme roles) (0) | 2020.09.09 |



댓글